Forex trading in South Africa is a popular form of investment. It is completely legal and South African Forex traders are protected by the Financial Sector Conduct Authority (FSCA). This beginner’s guide is intended to help South African residents learn how the Forex market works and how to get started trading.
What is Forex Trading?
Forex trading, derived from Foreign Exchange, is the process of exchanging one currency for another. Also called FX trading, Forex trading is a standard in international business and is used by financial institutions and investment banks to makes profits and hedge their other investments. Forex trading is also a popular form of investment for private citizens – called retail Forex traders – in South Africa.
How does the Forex market work?
The Forex market is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world, with a daily trading volume of approximately 100 trillion Rand (6.6 trillion USD – 2019). And Forex trading is buying and selling currencies on this market. A forex trader will buy a currency at the current market price and sell it again at a target price in the future. Because currency prices are always changing, the purchase and the sale price will be different, and the difference between the two prices will be the trader’s profit or loss.
It is only because of this market volatility that Forex traders can make a profit. Even though the Forex market operates 24 hours a day, market volatility tends to peak during the regular opening hours of the stock markets in Sydney, Tokyo, London and New York. The highest volume of trading generally occurs at the overlap of the London and New York opening hours, and this is when Forex traders are most active. Note that because South Africa is in approximately the same time zone as London, we are well placed geographically to take advantage of these market opens during regular working hours.
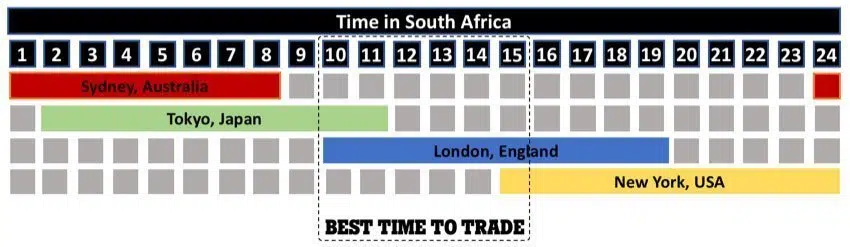
The only way for retail traders to access this international market is via an intermediary called a Forex broker. A Forex broker will provide the trading software and market access for their clients, so a trader can do market research and buy and sell currencies. These are the best brokers for beginner traders in South Africa.
How does Forex Trading work in South Africa?
In South Africa, Forex trading is regulated by the Financial Sector Conduct Authority (FSCA). The FSCA is responsible for protecting South African residents from financial fraud and ensuring a healthy, competitive financial marketplace. It oversees any company that provides a financial service including Forex brokers, banks, hedge funds, insurance companies and the Johannesburg Stock Exchange.
The FSCA is a good regulator, but Forex trading in South Africa is less regulated than in much of the world. Forex brokers here do not have to offer negative balance protection to their clients and do not have any limit on the amount of leverage they can offer. Therefore, South African traders have to be careful when trading that they do not lose more money than they have in their trading account.
FSCA-regulated Forex brokers are required to keep their clients’ money separated from company operating funds and are audited on a regular basis to ensure that client funds are not misused. All FSCA-regulated brokers must also apply for an Over-the-Counter Derivative Provider (ODP) licence, which further protects South African traders by ensuring that Forex brokers are managed by qualified directors and that they have enough money in reserve to avoid bankruptcy.
South African Forex traders can also take advantage of Rand (ZAR) trading accounts. Most Forex brokers only offer trading accounts in US Dollars (USD) or Euros (EUR). If a South African trader has a USD trading account, they lose money in currency conversion fees every time they deposit or withdraw money. With a ZAR trading account, there are no conversion fees. In addition, most ZAR trading accounts are kept in South African banks, so withdrawals and deposits are much faster.
Having your trading funds in a local bank also provides more security for South African traders. In the event of broker bankruptcy or closure, the FSCA can freeze the broker’s accounts and recover your funds (as was the case with JP Markets in 2020).
Advantages of Forex Trading
The most obvious advantage is the potential for high returns and financial freedom. Many Forex traders dream of making enough money to quit their day jobs. But not everyone will be able to do this. Traders have to develop new skills such as market analysis, data analysis, charting and a knowledge of how economic news impacts the Forex markets. Other advantages that Forex trading has over other forms of investment:
- Accessibility: Being able to invest online, either on your phone or your home computer. Almost anyone can trade Forex.
- 24 Hour Market: Unlike stock exchanges, the Forex market is open 24 hours a day, 5 days a week.
- Leverage: Forex trading is leveraged trading. With a relatively small amount of money, leverage allows traders to open large positions and amplify their profits.
- Short Selling: Forex traders can easily sell a currency pair and profit when the price goes down.
- Low Initial Cost: Forex trading is relatively low-cost to get started. Most brokers will only require the equivalent of a 100 USD deposit to open an account. Some brokers only require 5 or 10 USD.
Disadvantages of Forex Trading
The main disadvantage of Forex trading is the high level of risk involved. 60-90% of South African Forex traders lose money and profitable trading takes skill, education, discipline, and caution. Even professional traders will lose money, as the markets are never completely predictable. The main risks in Forex trading are:
- Leverage: Yes, also an advantage (see above). But, while a high level of borrowing will amplify your profits, it will also amplify your losses
- Unpredictable Volatility: In times of economic or political crisis currency prices can change quickly. Crisis events are often impossible to predict.
- Unregulated Brokers: Some brokers are unregulated, or poorly regulated. In the event of a dispute with an unregulated or poorly regulated broker, the trader is often powerless.
- High Trading Costs and Withdrawal Fees: Some brokers charge high trading fees or high withdrawal fees. High trading fees can turn a profitable trade into a losing trade. High withdrawals fees will also eat into profits.
The other disadvantage is the time needed to trade profitably. The best time to trade Forex in South Africa is during the daylight hours from Monday to Friday. This is also the time most people are at work. Forex trading can be a time-consuming activity and many beginner Forex traders don’t have the time to spend in front of their home computers all day.
Tips for Beginner Forex Traders
Before we get into the detail of how to trade Forex, here are some quick tips for beginner traders:
- Understanding how the Forex market works is essential. Without education, Forex trading is just gambling.
- Always use a demo account before you start trading with your own money
- Take courses on technical analysis, data analysis and market economics.
- If you are going to spend a lot of time trading a single currency pair, learn what moves that currency pair’s price and when these price changes happen.
- Always use a reputable and regulated Forex broker. Be sure to read the client contract terms and fine print.
- Be aware that most bonuses offered by Forex brokers cannot be withdrawn. These can only be used to supplement your trading account.
- Make sure that your chosen Forex broker offers negative balance protection. Without negative balance protection, you may end up owing your broker money after a heavy loss.
- Develop a trading strategy and test it with a demo account before you try it in the live market.
- Think carefully about how much money you want to put in your trading account. Never use more than you can afford to lose.
- Only ever risk a small percentage of your account balance at a time. Even if your trading strategy has a 70% win rate, if you risk a quarter of your money with every trade it only takes a small run of bad luck to wipe your account out.
- Use a stop-loss. It’s better to lose a small amount and try again tomorrow than lose everything.
- All Forex traders lose money, even professionals. When you make a losing trade don’t lose your discipline or discard your trading strategy. Consistency is essential.
Important Forex Trading Terms
- Pips: Pip stands for “Point in percentage”. In Forex trading, pips represent the fourth decimal place of a currency pair, except for the Japanese Yen where the pip represents the second decimal place. Pips are a unit of measure used to analyse price changes in a financial asset. The term is commonly used across all financial markets as a standard unit of measurement.
- Spread: The spread is the difference between the purchase price and the sale price of a financial asset and is measured in pips (see above). In Forex trading, the spread can be fixed or variable with variable spreads being more common.
- Lots: Lots are a standard unit for measuring trade volume in Forex trading. 1 lot represents 100,000 units of a currency pair: 1 lot of EUR/USD is €100,000 of the pair. One mini lot is 10,000 units of a pair and a micro lot is 1000 units of the pair.
- Margin: Your margin is your deposit made to hold open positions. It is a portion of your account capital that is held in reserve, like a deposit, representing a percentage of the total value of your trades.
- Leverage: Leverage is a term used by investors and traders to describe borrowing money from a broker to open a larger position in the market. With leverage, Forex traders can open positions many hundreds of times larger than the value of their capital. While leverage will amplify gains, it all also amplifies losses and needs to be managed carefully.
- Negative Balance Protection: This is a form of insurance. With leveraged trading, a bad loss can send your trading account negative. In this case, the trader will owe the broker the negative balance. Many brokers offer negative balance protection so traders never owe a broker money.
- Major Pairs: The major pairs are the most traded currency pairs in the world. There are 7 major currency pairs:
-
- EUR/USD (Euro/United States dollar) – the most traded pair
- USD/JPY (United States dollar/Japanese yen)
- GBP/USD (Great British Pound/United States dollar)
- AUD/USD (Australian dollar/United States dollar)
- USD/CAD (United States dollar/Canadian dollar)
- USD/CHF (United States dollar/Swiss franc)
- NZD/USD (New Zealand dollar/United States dollar
-
- CFDs: CFD is an acronym for Contract for Difference. CFDs are derivative instruments in which the value of the instrument is based on an underlying asset. When trading CFDs (whether Forex, indices, commodities or shares) neither the CFD broker nor the trader ever own the underlying asset.
How to Trade the Forex Market
A Forex trade has four main components – the asset, the size of the trade, the price, and the direction (buy or sell). Each of these is unique and affects the profitability of the trade.
The Asset: Currency pairs
In Forex trading, the asset is always a set of two currencies called a currency pair. Currencies are quoted in pairs, as the two currencies in a pair are bought and sold simultaneously. An example pair is the EUR/USD (euro/U.S. dollar).
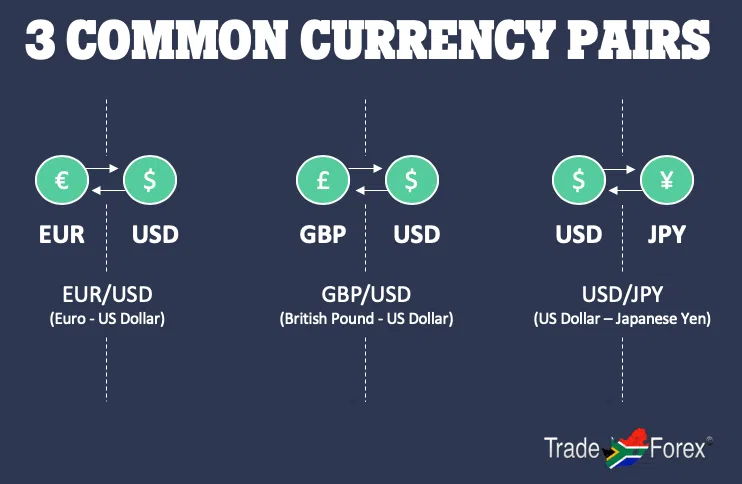
The first currency of any pair is called the base currency and the second currency is called the quote currency. In the ZAR/USD, the Rand is the base currency and the US Dollar is the quote currency. 
The Price: Forex quotes
The value of a currency is called a quote or a price. As currencies are quoted in pairs, the value of the quote currency is set in relation to the base currency.
For example, if the EUR/USD is priced at 1.1332, it means that 1 euro can be exchanged for 1.1332 US dollars. In Forex trading, the change in price of one currency relative to another is what generates a profit or loss.

Pips: Calculating price fluctuation
Price fluctuation (or the difference between two prices) is often measured and expressed as a value in pips. A pip is a small change in the value of a pair and is measured in the 4th decimal place; for example, if the EUR/USD trades at 1.1332, a one pip price increase would move the exchange rate to 1.1333.
There are exceptions to this rule, the most notable being Japanese yen quote pairs, such as USD/JPY, where a pip is a change in the 2nd decimal place.
Calculate It Yourself!
Quotes and Spreads: Ask price, bid price and trading costs
The value of a currency pair is expressed using a two-price quotation system: One price is for buying – or going long – and is called the ask price, this will be slightly above the market price. The other price is for selling – or going short – and is called the bid price, this will be slightly below the market price. The prices are set by your broker and the difference between the two is called the spread.
It’s best to see the spread as a broker’s fee for using its trading platform. The spread is measured in pips and is often the largest component of your trading costs. The spread is typically different for each currency pair and is influenced by factors like the pair’s liquidity, the broker’s mark-up and the broker type. Some brokers offer very tight spreads, often based on the raw interbank rate, and in these cases you will pay commission on every trade.
Here is an example of a 1-pip spread on the EUR/USD pair:
- Bid price:1.1332
- Ask price:1.1333
The ask price minus the bid price = 0.0001 = 1 pip.
Trade size: Lots, mini lots, micro lots and nano lots
The size or volume of a trade is measured in lots. This is similar to how stocks (equities) are measured in shares and gold, which is measured in ounces.
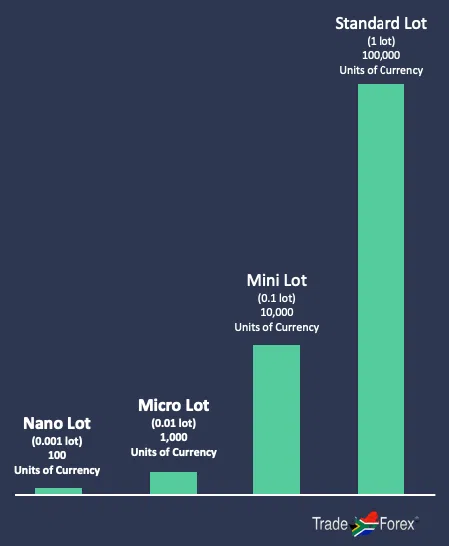
One standard lot is 100,000 units of a currency pair. So, if you buy one standard lot of the EUR/USD, you’re entering a trade worth 100,000 euro (which is more than USD 100,000).
One mini lot is 10,000 units of a pair. A mini lot of the EUR/USD is worth 10,000 euros.
One micro lot is 1,000 units of a pair. A micro lot of the EUR/USD is worth 1000 euro. In most cases, a micro lot is in most cases the smallest trade you can place, though some brokers will offer nano lots for smaller account types.
If you don’t know how to calculate the correct lot size for your trades or if you need help in calculating the pip-value for a certain lot size, take a look at How to Place My First Forex Trade.
Leverage: Amplifying exposure but increasing risk
Trading with leverage involves borrowing money from a liquidity provider to greatly increase the size of your trade. A trader will place a small deposit, known as the margin, and the rest of the trade value will be leverage. Your profit or loss will be based on the full value of the trade, not just your margin.
Most CFDs are traded with leverage because they allow traders to open much larger positions than their account balance would normally allow.

Using high leverage can increase your profit potential considerably but will also considerably increase your risk. Traders who use excessive leverage are exposing themselves to significant losses.
Here is an example to demonstrate how leverage can be used to place larger trades with less capital:
Let’s say you have a small trading account of USD 100. You have access to leverage of 1:500. You place a trade of 0.1 lots (one mini lot) on the USD/JPY pair. One mini lot is 10,000 units of the pair, which means the value of your trade is USD 10,000. Although the notional value of the trade is USD 10,000, only USD 20 of your account is engaged in opening the trade because 1:500 leverage means that you need to put down only 0.2%* of the notional amount of the trade.
*This example doesn’t consider the extra margin required to sustain a position with a floating loss.
Trade direction: Going long or going short
We touched on going long and going short earlier, but let’s look at what we mean in more detail.
CFD traders can speculate on whether an asset will increase or decrease in value and can profit either way. Profiting from the decreasing value of an asset is unique to CFD trading.
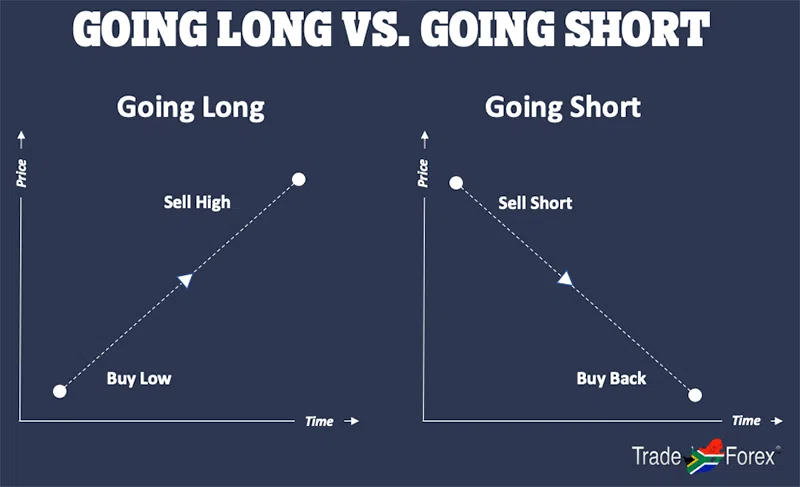
Long is the term used for buying, where the trader speculates that the price of the base currency will rise relative to the quote currency. In simple terms, you will make money from a long (buy) position if the price of the currency pair rises.
Short is the term for selling, where the trader speculates that the price of the base currency will fall relative to the quote currency. In simple terms, you will make money from a short (sell) position if the price of the currency pair declines.
Example – trading 1 micro lot on the EUR/USD
Let’s say your trading account is funded with USD 1000 and your account’s leverage is 1:100. The EUR/USD currency pair is trading at 1.20000. You speculate that the EUR will increase in value against the USD and you buy 1 micro lot at 1.20000. You set a stop loss at 1.19000 (100 pips below your entry price) and a take profit at 1.23000 (300 pips above your entry price). One micro lot (0.01 lots) is worth EUR 1,000, which is equivalent to USD 1200 in this scenario. As your account’s leverage is 1:100, only USD 12 of your account is used to open the position*.
*Extra margin is required to sustain a floating loss.
If your trade is correct
The euro strengthens against the U.S. dollar and hits your profit target at 1.23000. The 1000 euro you initially bought for USD 1200 is sold for USD 1230, which means you’ve made a profit of USD 30.
Another way to calculate your profit is to multiply the number of pips you’ve made by the pip value of a micro lot, which is USD 0.10 on the EUR/USD. So, 300 pips multiplied by USD 0.10 gives you a profit of USD 30.
If your trade goes wrong
The euro weakens against the U.S. dollar and hits your stop loss at 1.19000. The 1000 euro you initially bought for USD 1200 is sold for USD 1190, which means you’ve lost USD 10 on the trade.
Another way to calculate your loss is to multiply the number of pips you’ve made by the pip value of a micro lot, which is USD 0.10 on the EUR/USD. So, 100 pips multiplied by USD 0.10 gives you a loss of USD 10.
What is a Forex Trading Platform?
Some beginners assume that a Forex trading platform (also “trading platform” or “Forex platform” or just “platform”) is the same thing as a Forex broker. This is not true. Forex trading platforms are the software used to make trades, whereas Forex brokers are the companies that connect trading platforms to the Forex market.
- Forex trading platforms are the software used to make trades on the Forex market
- Forex brokers connect trading platforms to the Forex market
Which is the Best Forex Trading Platform?

Many traders believe that MetaTrader 4 (MT4) is the best trading platform because it is the most popular. Some traders think that MetaTrader 5 (MT5) is the best because it is newer and has more functions. Some traders think that cTrader is the best because it is easy-to-use but is very customisable.
Some Forex brokers also have their own platforms. They are usually web-based and are better suited to beginner traders as they have a simplified interface and fewer customisation options. The main problem with a broker’s own trading platform is that it can only be used with that one broker, whereas MT4, MT5 and cTrader can be used with many different Forex brokers.
MetaTrader 4
Metatrader 4 (MT4) is the most popular Forex trading platform in the world and is supported by most Forex brokers in South Africa. It is a third-party trading platform, which means that traders can use the same MT4 platform with different Forex brokers.
- MT4 is a high-speed and customisable trading platform, complete with a charting suite where charts can be overlaid with indicators from MT4’s library.
- MT4 allows users to build or buy expert advisors (or trading robots) and use them to automate their trading.
- MT4 is available on mobile, tablet, in a web browser and as a downloadable application.
MetaTrader 5
MetaTrader 5 (MT5) is the most recent version of the MetaTrader Forex trading platform. Unlike the basic version of MT4, MT5 allows trading on exchange-listed assets like stocks and ETFs. Though still not as popular as MT4, MT5 is supported by a growing number of Forex brokers.
- MT5 has more features than MT4 and comes with an Economic Calendar, Depth of Market indicator and an embedded chat function,
- Aso features unlimited chart windows, 80 built-in indicators and 12 more time-frames than MT4.
- MT5’s new scripting language is a more efficient language for building EAs
Unfortunately, MT5 is not backwards compatible with MT4, so any trading robots made for MT5 will not work in MT4 and vice versa.
cTrader
Launched in 2011, cTrader offers high-speed execution and is easier to use than MT4 and MT5. Like MT4 and MT5, cTrader is a third party trading platform, so traders can use their version of cTrader with multiple Forex brokers. cTrader Automate also lets traders build trading robots to automate their trading. Other cTrader features are:
- Detailed trade analysis, including the Analyse Tab, which provides an overview of the performance of your account
- Advanced platform customisation with cTrader Automate (formerly cAlgo)
- The ability to add multiple take-profit orders.
- Comprehensive educational videos available within the platform.
Most Forex brokers who offer cTrader don’t make money from the spread and will instead charge a commission per trade. Trading robots built for MT4 and MT5 will not function in cTrader.
Other Forex Trading Platforms
Some Forex brokers (like eToro or XTB) operate their own trading platforms and will not provide support for MT4, MT5 or cTrader. But most brokers with their own trading platforms will also support one of the third-party platforms. Broker’s own trading platforms tend to be easier to use for beginner traders as they have fewer functions, less customisability and simpler interfaces.
What Changes Forex Prices?
Like all markets, currency prices are set by supply and demand. But the constant shifts in supply and demand of the dozens of frequently traded currencies makes the Forex market more complex than most. Happily, there are a few indicators that traders can use to help them predict price movement.
Central Bank Economic Policy
National economic policy, set by central banks such as the Bank of England in the UK or the Federal Reserve in the USA, can have major effects on currency prices. Following the 2008 crash, some central banks engaged in quantitative easing or increasing the supply of money in circulation, which causes a currency’s price to drop. On the other hand, raising interest rates (usually used to combat inflation) will cause a currency’s price to increase as this leads to higher investor demand.
If economic policy changes without warning it can create major fluctuations in currency value. In 2015 the Swiss National Bank (SNB) abruptly scrapped the Swiss Franc’s peg to the Euro with no warning. This resulted in a huge increase in the value of the franc versus the euro – moving from 1.2 CHF/EUR to 0.86 within hours of the news.
Current Events
Current events can also affect the price of a currency. The Brexit debacle in the United Kingdom is a perfect example: Large investors like to move money into strong, predictable economies; so Brexit uncertainty caused institutional investors to move their capital out of the country, decreasing demand for the GBP and causing it to lose value. Once it appeared that the British Parliament had successfully agreed on a Brexit deal, the value of the GBP rose again.
You can see this effect anywhere you look in the world, if a good piece of economic news appears about a nation-state, its currency will increase in value. If the news is negative, the currency’s value will decrease. As a rule, the better health a country’s economy is in, the stronger and more stable its currency will be.
Trading Strategy
There are a few common strategies in Forex trading, the strategy that works for you will be dependent on your personality and lifestyle.
- Scalping: Scalping is when you open and close trades very quickly in times of very high volatility. The goal is to make lots of small profits over the course of the period of volatility. Scalping can be effective but requires a lot of free time and close attention to detail.
- Day Trading: Day traders open and close all their positions in a single day. Each day is treated as a new market. This trading strategy is less time-consuming than scalping but does require the skilful use of stop-loss and take-profits to be profitable.
- Swing Trading: Swing traders will often keep trades open for days or weeks at a time, making a profit from the general swings in the market. This is even less time-consuming than day trading but requires a good understanding of the normal movements of the currency pair being traded.
- Position Trading: Position traders keep their trading positions open the longest of all. This type of trade makes decisions based on economic fundamentals and can keep trades open for months or even years. While position trading is the least time-consuming trading strategy it requires a deep knowledge of global economics and extreme patience.
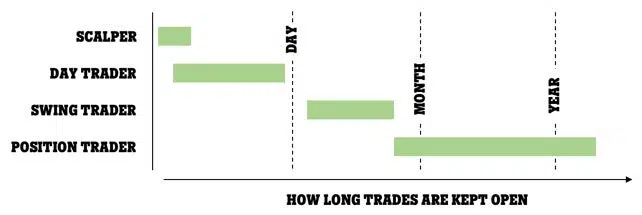
All trading strategies will require you to engage in market analysis in order to be successful. Market analysis can be grouped into two general types; fundamental analysis and technical analysis.
Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental analysis is the study of macroeconomic trends and their effects on price, this form of analysis requires a sound knowledge of economics and current events. In the broadest sense, Fundamental traders try to buy currencies from stronger economies at a low price and sell currencies from underperforming economies.
Fundamental traders are often reliant on scheduled news events that alter currency price. A good example is the Non-Farm Payroll (NFP) report in the United States; the NFP is released on the first Friday of every month and details how many jobs have been added or lost in the US economy. It’s generally seen as a good bellwether of US economic health and if the figure is higher or lower than expected then we will see increased volatility in the Forex market.
Fundamental analysis can be tough for traders unfamiliar with finance data but for traders who have a firm grasp of the financial news, and understand macroeconomics, this is a very successful approach.
Technical Analysis
Technical analysis is the prediction of future price action based on historical price data. Technical traders make heavy use of charts and will often rely on a variety of tools and indicators to help them identify trends and patterns. Almost all technical analysis is based on Dow Theory, a set of principles laid down in the 19th century by Charles Dow to describe and predict the movement of the stock market.
The most common form of technical analysis is price action trading, which is essentially the analysis of the actions of all the other market participants. Price action traders believe that market psychology is the main driver of price: They believe that there are many reasons for price movement, but that ultimately, its traders’ reactions to developments.
Technical analysis can be hard to learn, but once you have a good understanding of the basics it can be used in any financial market, not just the Forex market.
Analytical Tools
All good traders will use a combination of fundamental and technical analysis to find opportunities in the Forex market and there are several great tools we recommend to get you started:
- Autochartist: is a lightweight technical analysis tool that can be plugged directly into your trading platform. It analyses trends in price action and highlights trading opportunities based on automated technical analysis across a huge number of Forex pairs.
- Trading Central: A more robust analysis database that contains over 8,000 assets, including stocks, commodities and Forex pairings. Analysis, both technical and fundamental, provides data and commentary on each asset.
- TradingView: An intuitive and advanced financial visualisation platform and active social network for traders and investors. In addition, TradingView offers a huge number of HTML5 charts, stock screeners, hundreds of pre-built technical analysis indicators and a built-in news feed.
Whatever form of analysis you focus on, these tools will help you find your feet and do a lot of the hard work for you – especially on the technical side. Once you get to grips with technical analysis you will probably want to start customising your platform with indicators and algorithmic trading bots that can automate your trading strategy.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Forex Trading Legal in South Africa?
Yes, Forex trading is legal and regulated in South Africa. It is legal to trade with both local Forex brokers and brokers based overseas.
Is Forex Trading Taxable Income in South Africa?
Yes, Forex trading profits are taxable in South Africa. This is also true if you are trading with a Forex broker based overseas.
Is Forex Trading a Scam?
No, Forex trading is not a scam. But unfortunately, there are quite a few scammers in South Africa who take advantage of beginner Forex traders. Luckily, there are a few easy ways to avoid being scammed.
- Never give money to anyone you meet over social media (Facebook, Instagram, etc.)
- Learn to trade yourself, don’t give money to anyone to trade for you
- Make sure your Forex broker is regulated. You can check the FSCA register here.
- If it sounds too good to be true, it probably is. Don’t trust brokers or individuals that guarantee returns.
Conclusion
Some of these terms and concepts might be tricky to understand at first but it won’t take you long to get it when you see it in action. The best way to learn the basics of Forex trading is to practice on a demo account and place a few trades. Some brokers have local South African support teams, work with local SA banks, and offer support from their local offices either in Cape Town or
We still have plenty of good information waiting for you! Take a look at the articles below to further develop your skills and knowledge…
Essential reading
- The essential guide to learning Forex trading successfully is a must-read for any aspiring South African trader.
- How to place my first Forex trade.
Expect to learn a lot before trading profitably. You need to learn how to operate the software, do analysis, and manage the risk in the account. We have a Forex trading for beginners section to continue reading and explore many of the principles to succeed in trading. Here are articles most relevant to getting a good start.
- Technical Analysis vs Fundamental Analysis
- Pips are used for measuring changes in currency value. But how?
- Leverage can be used to grow your profits. Learn to calculate leverage needed
- Charts – Understanding Bar Charts, Volume & Time Comparisons
- How should I manage my risk with Stop Loss and Take Profit?
- Pivot points are a change in the direction of the market. Learn more about them for your trading.
- Forex Analysis Tools are crucial to success. Here are some of the more common ones







































