For over a decade, FxScouts.co.za has been reviewing forex brokers and provided in-depth analyses. Our extensive research and unique testing methodology ensures that all broker reviews are accurate and fair with hundreds of thousands of data points generated annually. Since 2012, we’ve tested over 180 brokers across global and South African markets. Our team of professionals are frequently cited in global and regional media, shaping market conversations and trends.
-
Best Forex Brokers
Our top-rated Forex brokers
-
Brokers for Beginners
Start trading here
-
Forex Demo Accounts
Learn to trade with no risk
-
ZAR Trading Accounts
Save on conversion fees
-
Lowest Spread Brokers
Raw spreads & low commissions
-
ECN Brokers
Trade with Direct Market Access
-
No-deposit Bonuses
Live trading with no deposit
-
High Leverage Brokers
Extend your buying power
-
Islamic Account Brokers
Best accounts for Muslim traders
-
Market Maker Brokers
Fixed spreads & instant execution
-
All Trading Platforms
Find a platform that works for you
-
TradingView Brokers
The top TradingView brokers
-
MetaTrader4 Brokers
The top MT4 brokers in SA
-
MetaTrader5 Brokers
The top MT5 brokers in SA
-
cTrader Brokers
The top cTrader brokers in SA
-
Forex Trading Apps
Trade on the go from your phone
-
Copy Trading Brokers
Copy professional traders
75-90% of retail traders lose money trading Forex and CFDs. You should consider whether you understand how CFDs and leveraged trading work and if you can afford the high risk of losing your money. We may receive compensation when you click on links to products we review. Please read our advertising disclosure. By using this website, you agree to our Terms of Service.
- FP Markets - Advanced trading tools, FSCA Regulation, and high-quality customer service
- Pepperstone - Wide range of trading platforms, low trading fees, and fast trade execution
- XM - Top-class education, exceptional market analysis, and a great bonus program
- Exness - Widest range of account options, ZAR Accounts, and 100+ Forex pairs
- Tickmill - Low Commissions, Fast and Free Deposits and Withdrawals, Great Bonus Program
- IC Markets - Excellent Regulation, Advanced Trading Tools, and 24/7 Customer Service
- Eightcap - Low Spreads and 100+ Crypto Pairs
- HFM - Low-cost Zero Account, Local Customer Support, and ZAR Trading Accounts
- Fusion Markets - Low Commissions, 24/7 Customer Support, and In-depth Market Analysis
Broker | Broker Score | Broker Website | Account Name | Min. Deposit | EUR/USD Spread | Commission | Trading Cost | Compare |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | 4.40 /5 Read Review | Visit Broker > 79% of retail CFD accounts lose money | RAW | AUD 100 | 0 pips | 6 USD / lot | USD 6 | |
 | 4.61 /5 Read Review | Visit Broker > 75.3% of retail CFD accounts lose money | cTrader Razor | USD 0 | 0.10 pips | 6 USD / lot | USD 7 | |
 | 4.45 /5 Read Review | Visit Broker > 75.33% of retail CFD accounts lose money | XM Ultra Low | USD 5 | 0.60 pips | Spread Only | USD 1 | |
 | 4.32 /5 Read Review | Visit Broker > 71.67% of retail CFD accounts lose money | Pro Raw Spread MT4 | USD 200 | 0 pips | 7 USD / lot | USD 7 | |
 | 4.58 /5 Read Review | Visit Broker > 70% of retail CFD accounts lose money | Raw | USD 100 | 0.10 pips | 6 USD/lot | USD 7 | |
 | 4.46 /5 Read Review | Visit Broker > 70.81% of retail CFD accounts lose money | RAW - MetaTrader | USD 200 | 0.02 pips | 7 USD / lot | USD 7.20 | |
4.53 /5 Read Review | Visit Broker > N/A of retail CFD accounts lose money | Raw | AUD 100 | 0.06 pips | 7 USD / lot | USD 7.60 | ||
 | 4.53 /5 Read Review | Visit Broker > 72.90% of retail CFD accounts lose money | Zero | USD 0 | 0.10 pips | 6 USD / lot | USD 7 | |
4.41 /5 Read Review | Visit Broker > 89% of retail CFD accounts lose money | Zero | AUD 0 | 0 pips | 4.5 USD/lot | USD 4.50 |
What is a Spread?
In forex trading, the “spread” refers to the difference between the buying price (Bid) and the selling price (Ask) of a currency pair. It’s essentially the cost of trading that the forex broker charges for providing their services.
Why are low spreads important?
- Cost Reduction: Low spreads can help traders to reduce their trading costs. Each time a trade is executed, the trader has to overcome the spread cost to get into a profitable position. The lower the spread, the less the price needs to move in the trader’s favour before they start to make a profit, and the less the price can move against the trader before they start to incur a loss.
- Higher Frequency Trading: Traders, especially those using high-frequency trading strategies like scalping and day trading, must enter and exit the markets frequently. Lower spreads mean they pay less to execute these trades.
- Increased Potential Profits: When the spread is lower, the distance to a profitable trade decreases. This can potentially increase a trader’s profitability, especially in volatile markets.
How we reviewed the brokers with the lowest spreads
At FXScouts, we have an experienced review team dedicated to evaluating Forex brokers. Our team of experts meticulously examines each broker in 7 different areas, amassing an enormous amount of data in the process. With over 200 individual metrics analysed, we invest hundreds of hours annually researching and scrutinising brokers to ensure that we only recommend the best in the Forex industry.
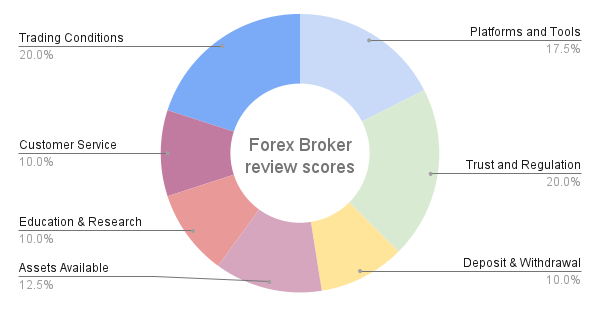
Of these 7 areas, we always prioritise regulation and costs. These are our priorities because traders want to know that their broker is trustworthy and isn’t overcharging them. Brokers are always altering the products they offer, and we keep our reviews updated with the latest data available. You can find out more about our in-depth review process here.
These are the lowest spread brokers in South Africa for 2024, as determined by our review process:
FP Markets – Advanced trading tools, FSCA Regulation, and high-quality customer service
FP Markets is an excellent choice for traders seeking a competitive trading environment with low trading fees and an advanced range of trading tools and platforms. FP Markets’ intuitive Trading App and consistently high-quality customer service further enhance its appeal. South African traders will also be pleased to note that in addition to ASIC and CySEC regulation, as of January 2023, FP Markets gained a licence from the South African FSCA, which means that SA client funds will be segregated at South African banks and that traders will benefit from local protection
- Low-cost Trading Accounts: FP Markets stands out for its Raw Account with a spread that starts at 0 pips (EUR/USD) in exchange for a low commission of 6 USD.
- Multiple Trading Platforms: Traders can select from various platforms, including MetaTrader 4, MetaTrader 5, cTrader, and TradingView catering to diverse trading preferences.
- Advanced Trading Tools: FP Markets has an impressive range of trading tools, including free Autochartist, VPS services, and the Trader’s Toolbox for an enhanced trading experience.
- Excellent Customer Service: FP Markets takes pride in its superior customer service, always ready to address trader queries with knowledgeable and prompt responses.
Pepperstone – Wide range of trading platforms, low trading fees, and fast trade execution
Pepperstone’s low-cost ECN trading service, fast trade execution, and range of third-party trading platforms have made it popular amongst experienced traders and serious beginners worldwide. More experienced traders who rely on scalping and bots for automated trading will appreciate that most trades on both Pepperstone’s accounts are executed in less than 30ms. With its commitment to transparency, trader education, and excellent customer service, Pepperstone consistently ranks among the best brokers for beginner and experienced traders.
- Regulation: Pepperstone is strongly regulated by top-tier authorities like the FCA and ASIC, ensuring that traders are treated fairly.
- Low Spreads: Pepperstone’s Razor Account has no minimum deposit and competitive spreads that average at 0.10 pips (EUR/USD)* in exchange for a reasonable commission of 7 USD per lot.
- Advanced Trading Platforms: Pepperstone offers access to the most reliable and popular trading platforms, including MT4, MT5, cTrader, and TradingView, which all have sophisticated tools and automated trading capabilities.
- Education and Market Analysis: Pepperstone stands out for its high-quality education and market analysis, with a huge range of articles, videos, and weekly interactive webinars.
*spreads correct as of November 2023
XM – Top-class education, exceptional market analysis, and a great bonus program
Renowned for some of the lowest fees in the industry, XM is a great choice for both beginner and more experienced South African traders. XM has some of the best educational and research resources in the industry and offers a number of low-cost, low-spread trading accounts, all with a minimum deposit requirement of 5 USD. XM further distinguishes itself with an expansive selection of trading tools and attractive bonuses and incentives for its traders.
- Low Fees: XM is known for its competitive fee structure, with a spread of 0.1 pips (EUR/USD) on its Zero Account in exchange for a commission of 7 USD.
- Exceptional Research and Education: XM provides excellent research and educational resources comprised of various sections, including its unique live education, daily Q&A sessions, videos, webinars, and Forex seminars.
- Beginner-Friendly Trading App: XM’s trading app is user-friendly and designed with the needs of beginners in mind, facilitating seamless trading on the go.
- Generous Bonuses and Incentives: XM keeps its traders engaged by offering attractive bonuses and incentives, including its no-deposit 30 USD bonus for new traders.
Exness – Widest range of account options, ZAR Accounts, and 100+ Forex pairs
Founded in 2009, Exness, a widely recognised broker, stands out with its versatile offering of nine distinct trading accounts. Its standout feature is the option for traders to open an account in ZAR, catering specifically to South African clients. Additionally, Exness offers an impressive selection of over 100 Forex pairs, surpassing many competitors’ offerings.
- Wide Range of Trading Accounts: Exness provides nine different trading accounts, accommodating diverse trading preferences and strategies.
- Low-cost Trading Account: Exness’s Pro Raw Spread accounts have a minimum deposit of 200 USD, with a spread of 0 pips (EUR/USD) and a commission of 7 USD.
- Account Opening in ZAR: Exness offers added convenience to South African traders by allowing them to open accounts in their local currency.
- Broad Forex Selection: With an extensive offering of over 100 Forex pairs, Exness provides a trading spectrum that significantly outpaces many competitors.
Tickmill – Low Commissions, Fast and Free Deposits and Withdrawals, Great Bonus Program
A reputable FSCA-regulated broker that has consistently demonstrated reliability and transparency, Tickmill boasts some of the industry’s lowest-commission trading accounts, making it a cost-effective choice for traders. Tickmill also offers swift, fee-free deposits and withdrawals, which improves traders’ profitability. New traders will be interested in Tickmill’s incentive program, which includes a 30 USD no-deposit bonus.
- Excellent Reputation: Tickmill’s solid reputation as a trustworthy broker stems from the fact that it is highly regulated by a number of top-tier authorities, including the UK’s FCA, CySEC of Cyprus, and the South African FSCA.
- Competitive Commissions: Tickmill stands out with two of the industry’s lowest commission accounts, the Pro Account, with a spread of 0 pips (EUR/USD) and a 4 USD (RT) commission and the VIP Account, also with a 0 pip spread, but a commission of 2 USD (RT), but with a minimum deposit of 10,000 USD.
- Fast and Free Deposits and Withdrawals: Tickmill offers fast and fee-free deposits and withdrawals and even has a Zero Fee policy, reimbursing traders for any third-party fees charged up to 100 USD on deposits of over 5,000 USD.
- Incentive Program: The Tickmill Welcome Account is a risk-free no-deposit trading account with 30 USD available to trade. Any South African resident can open it and it does not require full registration or identity verification.
IC Markets – Excellent Regulation, Advanced Trading Tools, and 24/7 Customer Service
With a high trust rating, IC Markets has catered well to its South African clients since its establishment in 2007. Renowned for its low trading costs, choice of platforms, and broad selection of trading tools, this broker also holds licenses from some of the world’s most reputable regulators. Beginners will appreciate the 24/7 exceptional customer support to assist with account setup and technical issues.
- High Trust Rating: IC Markets boasts a high trust rating, underpinning its credibility and reliability.
- Low Trading Costs: IC Markets offers a lower-cost trading environment than almost any other broker, with average spreads of 0.10 pips (EUR/USD) on its Raw Spread Account in exchange for a low commission of 6 USD (round turn) per lot.
- Choice of Platforms: With a range of trading platforms, including MT4, MT5, and cTrader, IC Markets caters to diverse trading preferences.
- Extensive Trading Tools: IC Markets offers a wide variety of tools, including VPS services, Trading Central, and various copy trading services.
- 24/7 Customer Support: IC Markets provides round-the-clock customer support, ensuring traders’ queries are addressed promptly.
Eightcap – Low Spreads and 100+ Crypto Pairs
A well-regulated global broker, Eightcap offers trading on multiple assets, including over 100 crypto pairs, has low trading fees, and a great choice of trading platforms, including MT4, MT5, and TradingView.
Raw Spread Account: Eightap provides customers with three account types. Its Raw Account boasts spreads of 0.1 pips (EUR/USD) in exchange for a commission of 7 USD, which is very competitive for the industry. The commission-free Standard and TradingView Accounts have a minimum deposit of 1oo USD and spreads that start at 1 pips (EUR/USD).
Wide Range of Trading Platforms: Eightcap offers its traders access to the widely acclaimed MetaTrader 4 and MetaTrader 5 platforms, in addition to TradingView, one of the most advanced and feature-rich trading platforms in the world.
Great Trading Tools: Eightcap offers a range of useful trading tools, including Capitalise.ai, which lets traders create automated trading strategies without coding knowledge, and ForexVPS for traders who deposit 1,000 USD.
HFM – Low-cost Zero Account, Local Customer Support, and ZAR Trading Accounts
A prominent international broker, HFM maintains a solid foothold in South Africa, setting itself apart with local FSCA regulation and support. Its unique offerings include ZAR trading accounts – a feature not common among many international brokers. Moreover, HFM facilitates rapid and free deposits and withdrawals in South African Rands through a network of local banks such as FNB, ABSA, Nedbank, and Standard Bank. For traders who value competitive, cost-effective trading conditions, advanced tools, and multiple platform options, HFM is a good option.
- Local Regulation and Support: Under the regulation of the FSCA, South Africans can rest assured that their funds are segregated at local banks and benefit from local protection. Local customer support further enhances the trader’s experience.
- ZAR Trading Accounts: HFM’s ZAR trading accounts set it apart from other international brokers, offering a unique advantage for South African traders who won’t have to pay currency conversion fees on deposits and withdrawals.
- Low-Cost Trading Accounts: HFM’s Zero Account has competitive spreads that start at 0 pips (EUR/USD) and a commission of 80 ZAR (6 USD) round turn with no required minimum deposit.
- Efficient and User-Friendly Trading App: The HFM Trading App stands out for its easy navigation and efficient operation, enabling smooth trading on the move.
Fusion Markets – Low Commissions, 24/7 Customer Support, and In-depth Market Analysis
Established in 2017, Fusion Markets has quickly carved out a space for itself in the competitive world of Forex trading, focusing on low-cost trading and excellent customer service. Fusion Markets offers two competitively priced account types accessible on both the MT4 and MT5 trading platforms. With an extensive news hub available from within its client portal, Fusion Markets’ market research far surpasses other brokers. Additionally, Fusion Markets ensures its clients can access their funds quickly and without cost, offering free and fast withdrawal options.
- Low-Cost Accounts: Fusion Markets stands out for its Zero Account, which has no minimum deposit requirement, spreads that start at 0 pips (EUR/USD), and a commission of just 4.5 USD (round turn).
- Great Research Tools: Fusion Markets provides a robust suite of research tools that can enhance the trading experience; these include Technical Insight, Analyst Views, and Market Buzz.
- 24/7 Customer Service: Its round-the-clock customer service ensures that assistance is always available.
- Free and Fast Withdrawals: Fusion Markets offers quick and free withdrawal options, providing easy access to traders’ funds.
How do brokers with low spreads make money?
In the world of forex trading and other types of investment, brokers typically earn money in one of two ways: through spreads and commissions.
A spread is the difference between the buying price and the selling price of a financial instrument. The spread is essentially the broker’s profit on each trade a trader makes.
On the other hand, a commission is a fee that a broker charges for its services. This is generally a flat fee per trade or a percentage of the total volume of the trade.
Now, let’s consider brokers who offer low spreads. These brokers essentially offer to execute trades at prices very close to the market price. This can be attractive to traders because it reduces their trading costs. However, because these brokers make less money from the spread, they may charge a commission to compensate for the lower profit margins.
The commission can be seen as a fee for the broker’s service of facilitating the trade. For a broker offering low or even zero spreads, the commission may be their primary source of income.
The Advantages and Disadvantages of Trading with Low Spreads
Trading with low spreads can have several advantages and disadvantages depending on your specific trading strategy and trading frequency. Here’s a breakdown of these aspects:
Advantages
- Lower Transaction Costs: Low spreads mean that the difference between a financial instrument’s bid (buy) price and the ask (sell) price is smaller. This results in lower transaction costs for the trader, especially for those engaged in high-frequency trading, such as day traders or scalpers. This can increase the net profit from each trade.
- Predictable Costs: Brokers with low spreads typically charge a fixed commission per trade, making the cost of trading predictable. This can be particularly useful for traders who trade in large volumes, as the commission fee does not increase proportionally with the trade size, unlike the cost related to spreads.
- Transparent Pricing: Low spreads coupled with a commission-based pricing model tend to be more transparent. The broker makes money from the commission, and the spreads are closer to the underlying market prices. This can provide a clearer view of the market conditions and facilitate better trading decisions.
Disadvantages
- Commissions Can Add Up: While the lower spread can reduce transaction costs, adding a commission fee on every trade can add up, especially for high-frequency traders. Therefore, the total cost of trading might not be lower than a higher spread, no-commission model, particularly for less active traders.
- Costly for Less Active Traders: For traders who don’t trade as frequently, paying a commission on every trade can become more costly than simply dealing with a higher spread. This is because the commission is charged on every trade, regardless of size, which can eat into profits for smaller or less frequent trades.
- Complex Fee Structure: Understanding and calculating costs can be more complex with a low spread and commission model. Traders need to consider both the spread and the commission in their cost analysis, which can be confusing, particularly for novice traders.
Whether a low spread and commission model is advantageous depends largely on the trader’s strategy and trading frequency. Each trader must understand their own trading habits, calculate their potential costs under different pricing models, and choose the broker that offers the most cost-effective solution for their specific needs.
How Do You Compare Low Spread Accounts?
When comparing brokers with low-spread accounts, looking beyond your trading costs is essential. Direct trading costs aren’t the only factor to consider when opening a trading account. Brokers with low-spread accounts often have other ways of generating revenue. Here are some factors to consider:
- Regulatory Oversight: Ensure the broker is regulated by a reputable financial authority. Regulation provides a level of security and can help safeguard your investment.
- Trading Platform: Assess the broker’s trading platform for ease of use, reliability, and available tools and features. Good trading platforms should be intuitive and stable and offer helpful features like charting tools and real-time data feeds.
- Execution Speed: A good broker should execute trades quickly and at the price you expect. Delays in execution can lead to trades being filled at a less desirable price.
- Customer Service: Excellent customer service is essential, particularly if you encounter technical issues or have questions about your account. Look for brokers who offer swift, knowledgeable, and accessible customer service.
- Additional Fees: Some brokers may charge deposits, withdrawals, or account inactivity fees. Be sure to consider these costs when evaluating different brokers.
By carefully evaluating each of these factors, you can compare brokers with low-spread accounts more effectively and make a choice that suits your trading style and goals.
FAQs
What is considered a low spread at Forex brokers?
In the world of Forex trading, a spread is considered low if it’s close to 0.0 pips. However, what constitutes a ‘low’ spread can depend on the currency pair being traded. For major currency pairs like EUR/USD, a low spread is typically anything under 1 pip. For less liquid currency pairs like the minors or exotics like the USD/ZAR, spreads are usually considerably wider.
What is considered a low commission for a Forex broker account?
Commission rates can vary widely among Forex brokers, but a low commission is typically considered to be around 0.1% – 0.3% of the trade volume. In terms of fixed commissions, which are more common in ECN or STP brokers, anything around $6 – $10 per lot traded (100,000 units of currency) could be considered low.
Do some brokers offer zero-spread accounts?
Yes, some brokers offer zero-spread accounts. Zero-spread forex brokers offer trading accounts where a currency pair’s bid and ask price are the same. This means there is no difference between the bid price and the ask price of a currency pair. However, it’s essential to note that while the spread is zero, these brokers often compensate by charging a commission on trades or using other fee structures. Therefore, traders must understand the overall cost of trading, not just the spread, before choosing a broker.
Are low-spread accounts suitable for all traders?
While low-spread accounts can save costs for high-volume traders, they might not be as beneficial for less active traders. This is because the commission costs could outweigh the benefits of low spreads for traders who don’t trade frequently.
Which Forex broker has the tightest spread?
The broker with the tightest spread is not constant, as spreads fluctuate based on market conditions and the broker’s policies. However, brokers that consistently offer tight spreads often operate using an Electronic Communication Network (ECN) or Straight Through Processing (STP) model.
Can I trade Forex without a broker?
While it is technically possible to trade forex without a broker, it’s not practical for most individuals. Brokers provide access to the trading platforms and the liquidity necessary to trade efficiently in the forex market.
What’s the Difference Between Raw Spread and a Standard Account?
A standard account typically includes all trading costs within the spread. This means you won’t pay a separate commission on your trades. On the other hand, a raw spread account usually offers spreads close to zero, with brokers charging a separate commission on each trade. The choice between the two often depends on the trader’s strategy and volume of trades.
Which currency pairs have the lowest spreads?
The most heavily traded pairs, such as the EUR/USD, GBP/USD and USD/JPY, normally have the lowest spreads, while an emerging-market currency paired with the USD, such as the USD/ZAR, will have a wider spread. In other words, the more liquid the market, the narrower the spread. That’s because the high volumes traded generate lots of profit for brokers, even though the profit margins might be narrow.
Forex Risk Disclaimer
Trading Forex and CFDs is not suitable for all investors as it carries a high degree of risk to your capital: 75-90% of retail investors lose money trading these products. Forex and CFD transactions involve high risk due to the following factors: Leverage, market volatility, slippage arising from a lack of liquidity, inadequate trading knowledge or experience, and a lack of regulatory protection. Traders should not deposit any money that is not considered disposable income. Regardless of how much research you have done or how confident you are in your trade, there is always a substantial risk of loss. (Learn more about these risks from the UK’s regulator, the FCA, or the Australian regulator, ASIC).
Our Rating & Review Methodology
Our Broker Awards and Forex Rankings Report and Directory of CFD Brokers to Avoid are the result of extensive research on over 180 Forex brokers. These resources help traders find the best Forex brokers – and steer them away from the worst ones. These resources have been compiled using over 200 data points on each broker and over 3000 hours of research. Our team conducts all research independently: Testing brokers, gathering information from broker representatives and sifting through legal documents. Learn more about how we rank brokers.
Editorial Team

Chris Cammack
Head of Content
Chris joined the company in 2019 after ten years experience in research, editorial and design for political and financial publications. His background has given him a deep knowledge of international financial markets and the geopolitics that affects them. Chris has a keen eye for editing and a voracious appetite for financial and political current affairs. He ensures that our content across all sites meets the standards of quality and transparency that our readers expect.

Alison Heyerdahl
Senior Financial Writer
Alison joined the team as a writer in 2021. She has a medical degree with a focus on physiotherapy and a bachelor’s in psychology. However, her interest in forex trading and her love for writing led her to switch careers, and she now has over eight years experience in research and content development. She has tested and reviewed 100+ brokers and has a great understanding of the Forex trading world.

Ida Hermansen
Financial Writer
Ida joined our team as a financial writer in 2023. She has a degree in Digital Marketing and a background in content writing and SEO. In addition to her marketing and writing skills, Ida also has an interest in cryptocurrencies and blockchain networks. Her interest in crypto trading led to a wider fascination with Forex technical analysis and price movement. She continues to develop her skills and knowledge in Forex trading and keeps a close eye on which Forex brokers offer the best trading environments for new traders.
Stay updated
This form has double opt in enabled. You will need to confirm your email address before being added to the list.